On Friday April 15, GitHub Security announced it had detected the compromise of OAuth access tokens issued to Heroku and Travis-CI integrations to download data from dozens of organizations. Many private repositories had been compromised, including those belonging to npm and GitHub itself.
It's certainly not the first time OAuth access tokens have been stolen and abused for intrusions. For instance, on July 7, 2020, hackers stole GitHub and GitLab OAuth tokens from Git analytics firm Waydev. Third party apps and plugins can be leveraged by adversaries as a software supply chain attack vector and should always be treated with caution.
This post will cover the details behind this attack, its potential risks, and what organizations can do to protect themselves.
GitHub OAuth Token attack
On April 12, GitHub Security identified unauthorized access to their NPM production infrastructure using a compromised AWS API key. After further investigation, they concluded that a malicious actor had obtained this key when downloading a set of private npm repositories using a stolen OAuth token from either Heroku or Travis-CI. Both serve as 3rd party OAuth applications and provide various CI/CD capabilities by integrating with SCMs such as GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket. The applications maintained by these integrators were used by GitHub users, including GitHub itself.
The compromised OAuth user tokens were stolen and abused to download private repositories belonging to dozens of victim organizations using Heroku and Travis-CI-maintained OAuth applications. The suspicion is that the actors were, and possibly still are, scanning the downloaded private repository contents (to which the stolen OAuth token had access) for secrets that could be used to expand into other infrastructure inside the organization.
On April 13 and 14, GitHub revoked access tokens associated with GitHub and npm’s internal use of these compromised applications. Moreover, they disclosed their findings to Heroku and Travis-CI and requested that they initiate their own security investigations, revoke all OAuth access tokens associated with the affected applications, and begin work to notify their own users.
The potential risk of A Token Attack
Since an authorized OAuth App has access to all of its user's or organization owner's accessible resources, a compromised OAuth app could lead to a severe software supply chain attack.
For example, say you’re using Travis-CI as a build platform within your organization. This actually means that Travis-CI has an OAuth access token with all of the permissions that the user who issued the Travis-CI integration has. So if Travis-CI’s infrastructure gets compromised and an attacker manages to obtain that token (e.g., by gaining access to the database where they keep customers’ tokens) – all the repositories under the integrating user account will be subject to the attacker’s will. For example, the attacker could download the git repositories, scan for sensitive secrets, laterally move to additional organization resources and cloud services, or inject malicious payloads to the organization repositories and artifacts to initiate a supply chain attack.
Should I be worried?
GitHub mentioned it is working to identify and notify all known-affected victims and organizations discovered through their analysis across GitHub.com. But if you want to be confident, it is advised you do the following:
- Make sure you’re not using any compromised OAuth app by following GitHub’s documentation
- Review your organization’s audit logs for unexpected or anomalous activity
- Review your user account security logs for unexpected or anomalous activity
It’s important to note that it is possible that GitHub users were not the only victims of this attack. If the compromised Heroku or Travis-CI tokens also contained OAuth applications of other services, such as GitLab, the assets of those services might be compromised as well. So we recommend users of all SCMs that can integrate with Heroku and Travis-CI run their appropriate validations.
Mitigate GitHub Access Token Risk
To keep yourself protected from this kind of attacks, we recommend the following security measures:
- Enable OAuth App access restrictions for your organization. This will allow you to prevent untrusted apps from accessing the organization's resources while allowing organization members to use OAuth Apps for their personal accounts.
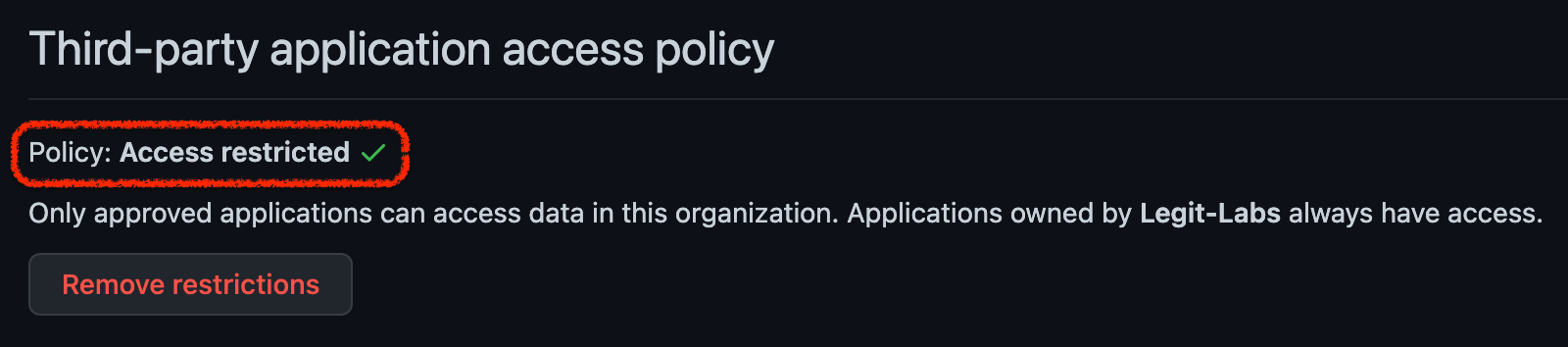
- Periodically review which OAuth apps are authorized in your organization and whether their permissions are appropriate and adhere to least privilege principle.
- OAuth applications are not the only way to integrate with 3rd party services. This can also be done via GitHub apps, which are not tightly coupled to the user who created them. A GitHub app allows restricted access to only selected repositories, and with limited scope, as opposed to having access to all of its user’s accessible resources, and is therefore more recommended.
- Just in case your access tokens get compromised, and your repositories are being scanned by malicious actors, always make sure your codebase remains secrets-free by running a secret detection tool. This will prevent the attacker from obtaining lateral movement and increasing their blast radius.
We’re Here To Help
The principles of securing your SDLC pipeline may appear straightforward, but in practice it gets complicated and time-consuming quickly, especially as your organization scales. Legit Security aims to make the process of securing your SDLC much easier, and we’ve developed a SaaS-based platform to do just that. We can help you make sure the aforementioned mitigation steps are covered by your SCM, be it GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket and more. Contact us if you’d like to learn more.
To learn more best practices in software supply chain security, check out our guide: Best Practices to Secure Your Software Supply Chains.
